TLC272
- Trimmed Offset Voltage:
TLC277 . . . 500 uV Max at 25°C, VDD = 5 V - Input Offset Voltage Drift ...Typically 0.1 uV/Month, Including the First 30 Days
- Wide Range of Supply Voltages Over Specified Temperature Range:
0°C to 70°C ...3 V to 16 V
–40°C to 85°C ...4 V to 16 V
–55°C to 125°C ...4 V to 16 V - Single-Supply Operation
- Common-Mode Input Voltage Range Extends Below the Negative Rail (C-Suffix, I-Suffix types)
- Low Noise ...Typically 25 nV/
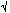 Hz at f = 1 kHz
Hz at f = 1 kHz - Output Voltage Range Includes Negative Rail
- High Input impedance ...1012
 Typ
Typ - ESD-Protection Circuitry
- Small-Outline Package Option Also Available in Tape and Reel
- Designed-In Latch-Up Immunity
LinCMOS is a trademark of Texas Instruments.
The TLC272 and TLC277 precision dual operational amplifiers combine a wide range of input offset voltage grades with low offset voltage drift, high input impedance, low noise, and speeds approaching those of general-purpose BiFET devices.
These devices use Texas Instruments silicon-gate LinCMOS™ technology, which provides offset voltage stability far exceeding the stability available with conventional metal-gate processes.
The extremely high input impedance, low bias currents, and high slew rates make these cost-effective devices ideal for applications previously reserved for BiFET and NFET products. Four offset voltage grades are available (C-suffix and I-suffix types), ranging from the low-cost TLC272 (10 mV) to the high-precision TLC277 (500 uV). These advantages, in combination with good common-mode rejection and supply voltage rejection, make these devices a good choice for new state-of-the-art designs as well as for upgrading existing designs.
In general, many features associated with bipolar technology are available on LinCMOS™ operational amplifiers without the power penalties of bipolar technology. General applications such as transducer interfacing, analog calculations, amplifier blocks, active filters, and signal buffering are easily designed with the TLC272 and TLC277. The devices also exhibit low voltage single-supply operation, making them ideally suited for remote and inaccessible battery-powered applications. The common-mode input voltage range includes the negative rail.
A wide range of packaging options is available, including small-outline and chip carrier versions for high-density system applications.
The device inputs and outputs are designed to withstand –100-mA surge currents without sustaining latch-up.
The TLC272 and TLC277 incorporate internal ESD-protection circuits that prevent functional failures at voltages up to 2000 V as tested under MIL-STD-883C, Method 3015.2; however, care should be exercised in handling these devices as exposure to ESD may result in the degradation of the device parametric performance.
The C-suffix devices are characterized for operation from 0°C to 70°C. The I-suffix devices are characterized for operation from –40°C to 85°C. The M-suffix devices are characterized for operation over the full military temperature range of –55°C to 125°C.
技术文档
| 类型 | 标题 | 下载最新的英语版本 | 日期 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| * | 数据表 | LinCMOS Precision Dual Operational-Amplifiers 数据表 (Rev. E) | 2002年 2月 25日 | |||
| * | 勘误表 | Errata for TLC272/2A/2B/2Y/77 Data Sheet SLOS091E: Error in Elec Characteristics | 2011年 4月 13日 | |||
| 电子书 | The Signal e-book: 有关运算放大器设计主题的博客文章汇编 | 英语版 | 2018年 1月 31日 | |||
| 应用手册 | TLC272 and TLC277 EMI Immunity Performance | 2013年 12月 31日 |
设计和开发
如需其他信息或资源,请点击以下任一标题进入详情页面查看(如有)。
AMP-PDK-EVM — 放大器高性能开发套件评估模块
放大器高性能开发套件 (PDK) 是一款用于测试常见运算放大器参数的评估模块 (EVM) 套件,与大多数运算放大器和比较器均兼容。该 EVM 套件提供了一个主板,主板上具有多个插槽式子卡选项以满足封装需求,使工程师能够快速评估和验证器件性能。
AMP-PDK-EVM 套件支持五种常用的业界通用封装,包括:
- D(SOIC-8 和 SOIC-14)
- PW (TSSOP-14)
- DGK (VSSOP-8)
- DBV(SOT23-5 和 SOT23-6)
- DCK(SC70-5 和 SC70-6)
DIP-ADAPTER-EVM — DIP 适配器评估模块
借助 DIP-Adapter-EVM 加快运算放大器的原型设计和测试,该 EVM 有助于快速轻松地连接小型表面贴装 IC 并且价格低廉。您可以使用随附的 Samtec 端子板连接任何受支持的运算放大器,或者将这些端子板直接连接至现有电路。
DIP-Adapter-EVM 套件支持六种常用的业界通用封装,包括:
- D 和 U (SOIC-8)
- PW (TSSOP-8)
- DGK(MSOP-8、VSSOP-8)
- DBV(SOT23-6、SOT23-5 和 SOT23-3)
- DCK(SC70-6 和 SC70-5)
- DRL (SOT563-6)
DUAL-DIYAMP-EVM — 双通道通用自制 (DIY) 放大器电路评估模块
DUAL-DIYAMP-EVM 系列可实现快速、方便的原型设计,并且使用常用的 0805 或 0603 (...)
ANALOG-ENGINEER-CALC — 模拟工程师计算器
CIRCUIT060013 — 采用 T 网络反馈电路的反相放大器
CIRCUIT060074 — 采用比较器的高侧电流检测电路
PSPICE-FOR-TI — 适用于 TI 设计和模拟工具的 PSpice®
借助 PSpice for TI 的设计和仿真环境及其内置的模型库,您可对复杂的混合信号设计进行仿真。创建完整的终端设备设计和原型解决方案,然后再进行布局和制造,可缩短产品上市时间并降低开发成本。
在 PSpice for TI 设计和仿真工具中,您可以搜索 TI (...)
TINA-TI — 基于 SPICE 的模拟仿真程序
TINA-TI 安装需要大约 500MB。直接安装,如果想卸载也很容易。我们相信您肯定会爱不释手。
TINA 是德州仪器 (TI) 专有的 DesignSoft 产品。该免费版本具有完整的功能,但不支持完整版 TINA 所提供的某些其他功能。
如需获取可用 TINA-TI 模型的完整列表,请参阅:SpiceRack - 完整列表
需要 HSpice (...)
PMP8740 — 满载效率为 92% 的 2kW 工业交流/直流电池充电器参考设计
TIDA-00200 — 面向电池充电应用的 120V AC 输入·200W 交错反激式
| 封装 | 引脚 | CAD 符号、封装和 3D 模型 |
|---|---|---|
| PDIP (P) | 8 | Ultra Librarian |
| SOIC (D) | 8 | Ultra Librarian |
| SOP (PS) | 8 | Ultra Librarian |
| TSSOP (PW) | 8 | Ultra Librarian |
订购和质量
- RoHS
- REACH
- 器件标识
- 引脚镀层/焊球材料
- MSL 等级/回流焊峰值温度
- MTBF/时基故障估算
- 材料成分
- 鉴定摘要
- 持续可靠性监测
- 制造厂地点
- 封装厂地点